- Joined
- Apr 27, 2009
- Messages
- 173
- Reaction score
- 0
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature.
a.) The reaction with the larger activation energy will be faster. (Right)
b.) The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster.
How?
If you do Arrhenius equation:
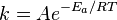 Increase the EA to say 500...then k goes to zero. Smaller k means smaller reaction rate.
Increase the EA to say 500...then k goes to zero. Smaller k means smaller reaction rate.
Put the EA at 5 and k is a small number greater than zero. So the reaction rate is higher than the larger Ea.
Also, just from common sense it seems that a lower activation energy would make any reaction a faster reaction. Please help me, thank you!
a.) The reaction with the larger activation energy will be faster. (Right)
b.) The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster.
How?
If you do Arrhenius equation:
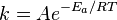
Put the EA at 5 and k is a small number greater than zero. So the reaction rate is higher than the larger Ea.
Also, just from common sense it seems that a lower activation energy would make any reaction a faster reaction. Please help me, thank you!
Last edited:
