- Joined
- Apr 29, 2011
- Messages
- 2,171
- Reaction score
- 863
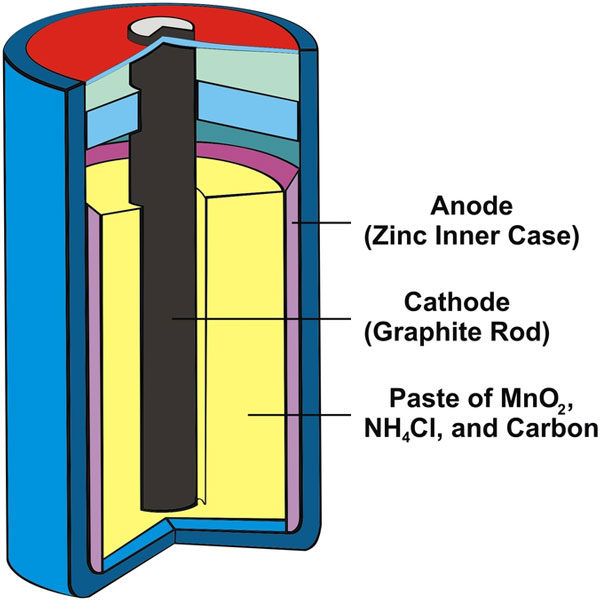
I understand that electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Here, from this picture, it would seem like electrons flow from the outside (where the anode is) to the cathode (core)?
But does this only happen at the top and bottom of the battery where they possibly come into contact? (I'm not sure where exactly they contact)?
Also, how do you ensure that the top is positive and the bottom is negative using this setup?
But does this only happen at the top and bottom of the battery where they possibly come into contact? (I'm not sure where exactly they contact)?
Also, how do you ensure that the top is positive and the bottom is negative using this setup?

