The answer indicated by the filled-in circle is mine, which is wrong. Please give explanations for the right answers, if possible. Thank You...
B. Decreased bone formation due to inhibition of osteoblast differentiation
C. Increased bone resorption due to decreased calcium absorption
D. Increased bone resorption due to decreased serum parathyroid hormone concentration
E. Increased bone resorption due to estrogen receptor defect
A 49-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of fever, shortness of breath, and confusion. She is a postal worker. Her temperature is 38.4°C (101.2°F), respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Physical examination shows nuchal rigidity. Breath sounds are decreased on the right side of the chest. A lumbar puncture is done. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows: Glucose: 18 mg/dL
Total protein: 138 mg/dL
Leukocyte count: 638/mm3
Segmented neutrophils: 87%
Monocytes: 13%
RBC: 2300/mm3
B. Glucuronoxylomannan
C. Hyaluronic acid
D. Polyglutamic acid
E. Polyribitol phosphate
B. Benztropine
C. Levodopa
D. Ropinirole
E. Selegiline
A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 10-day history of yellow skin, vague abdominal discomfort, and fatigue. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows generalized icterus. Serum studies show:AST: 320 U/L
ALT: 340 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg): positiveIgM
anti-hepatitis B core antigen(HBcAg): positive
Anti-hepatitis D virus: negative
B. Antibody against HBsAg
C. Complement via the alternate pathway
D. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
E. Viral cytopathic effect
A 6-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 2-week history of increased thirst and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight loss. Her mother says that the patient is constantly drinking water. She is at the 75th percentile for height and 50th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows tachypnea and dehydration. Laboratory studies show hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketonemia. If a biopsy specimen were obtained from this patient's pancreas, which of the following findings in islet cells would now be most likely? A. Basement membrane thickening of capillaries
B. Cellular necrosis and lymphocytic infiltration
C. Decrease in mass and deposition of amyloid
D. Large β cells and nuclei
E. Marked atrophy and fibrosis
Two programs for the treatment of patients with newly detected hypercholesterolemia were tried in a community. Program A was used in one district of the community, and Program B was used in another. After four years, 45% of the 2200 patients on Program A and 49% of the 1900 patients on Program B had been successfully treated for hypercholesterolemia. The difference between the success rates for the two programs was statistically significant (p < .01). Health officials, however, decided not to change to Program B in the first district because the magnitude of the difference was so small. Which of the following best explains their decision? A. They attributed the difference in success rates to chance alone
B. They distinguished between statistical significance and practical importance of the difference in success rates
C. They felt the p value was too small to justify a decision in favor of Program B
D. They felt the samples were too small to justify a decision in favor of Program B
During a 5-year study at a hospital, data about antimicrobial drug use for respiratory infections and antimicrobial susceptibility for respiratory isolates are compiled. At the end of 5 years, the data show that levofloxacin was the most common drug used to treat respiratory infections and that its usage increased significantly since the beginning of the study. Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to levofloxacin increased from 20% to 54% during the 5-year period. Based on these data, there is a greater likelihood of detecting which of the following in the latter isolates compared with the bacteria recovered at the beginning of the study? A. Expression of AmpC β-lactamases
B. Expression of carbapenemase
C. Expression of extended-spectrum β-lactamases
D. Mutation of the gene encoding dihydrofolate reductase
E. Mutation of the gene encoding elongation factor-2
F. Mutation of the gene encoding topoisomerase II
The graph shows the response elicited by different concentrations of drug X in a system containing spare receptors in the absence (solid curve) and presence (dashed curves) of two different concentrations of drug Y. Drug Y alone has no effect.
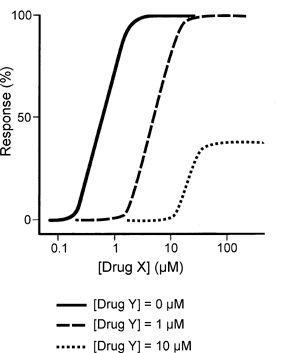
Which of the following best describes drug Y?
A. Competitive reversible antagonist
B. Full agonist
C. Inverse agonist
D. Noncompetitive antagonist
E. Partial agonist
Glucose: 117 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1 mg/dL
Total cholesterol: 227 mg/dL
HDL-cholesterol: 32 mg/dL
Triglycerides: 347 mg/dL
AST: 87 U/L
ALT: 85 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's increased serum liver enzyme activity?
A. Alcoholic hepatitis
B. Hemochromatosis
C. Hepatitis A
D. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
E. Porphyria cutanea tarda
A 76-year-old woman comes to the physician because of severe back pain for the past 2 weeks. She has no history of smoking. She has been taking prednisone (30 mg/day) for rheumatoid arthritis for the past 6 months and has received hormone replacement therapy with estrogen and progesterone for the past 15 years. Calcium and vitamin D intake are adequate. X-rays of the spine show a vertebral fracture. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the fracture?
A. Decreased bone formation due to decreased calcium absorption B. Decreased bone formation due to inhibition of osteoblast differentiation
C. Increased bone resorption due to decreased calcium absorption
D. Increased bone resorption due to decreased serum parathyroid hormone concentration
E. Increased bone resorption due to estrogen receptor defect
A 49-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of fever, shortness of breath, and confusion. She is a postal worker. Her temperature is 38.4°C (101.2°F), respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Physical examination shows nuchal rigidity. Breath sounds are decreased on the right side of the chest. A lumbar puncture is done. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows:
Total protein: 138 mg/dL
Leukocyte count: 638/mm3
Segmented neutrophils: 87%
Monocytes: 13%
RBC: 2300/mm3
A Gram stain of CSF shows large, gram-positive, spore-forming bacilli. A chest x-ray shows marked widening of the mediastinum. Which of the following extracellular virulence factors most likely enables the causal organism to evade phagocytosis?
A. Alginate B. Glucuronoxylomannan
C. Hyaluronic acid
D. Polyglutamic acid
E. Polyribitol phosphate
A 45-year-old man with recently diagnosed early-onset Parkinson disease comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He has a long history of major depressive disorder successfully treated with fluoxetine. Treatment with which of the following antiparkinsonian drugs is contraindicated in this patient?
A. Amantadine B. Benztropine
C. Levodopa
D. Ropinirole
E. Selegiline
A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 10-day history of yellow skin, vague abdominal discomfort, and fatigue. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows generalized icterus. Serum studies show:
ALT: 340 U/L
Hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg): positiveIgM
anti-hepatitis B core antigen(HBcAg): positive
Anti-hepatitis D virus: negative
Direct damage to infected hepatocytes in this patient is most likely mediated predominantly by which of the following?
A. Antibody against HBcAg B. Antibody against HBsAg
C. Complement via the alternate pathway
D. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
E. Viral cytopathic effect
A 6-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 2-week history of increased thirst and a 3-kg (6.6-lb) weight loss. Her mother says that the patient is constantly drinking water. She is at the 75th percentile for height and 50th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows tachypnea and dehydration. Laboratory studies show hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketonemia. If a biopsy specimen were obtained from this patient's pancreas, which of the following findings in islet cells would now be most likely?
B. Cellular necrosis and lymphocytic infiltration
C. Decrease in mass and deposition of amyloid
D. Large β cells and nuclei
E. Marked atrophy and fibrosis
Two programs for the treatment of patients with newly detected hypercholesterolemia were tried in a community. Program A was used in one district of the community, and Program B was used in another. After four years, 45% of the 2200 patients on Program A and 49% of the 1900 patients on Program B had been successfully treated for hypercholesterolemia. The difference between the success rates for the two programs was statistically significant (p < .01). Health officials, however, decided not to change to Program B in the first district because the magnitude of the difference was so small. Which of the following best explains their decision?
B. They distinguished between statistical significance and practical importance of the difference in success rates
C. They felt the p value was too small to justify a decision in favor of Program B
D. They felt the samples were too small to justify a decision in favor of Program B
During a 5-year study at a hospital, data about antimicrobial drug use for respiratory infections and antimicrobial susceptibility for respiratory isolates are compiled. At the end of 5 years, the data show that levofloxacin was the most common drug used to treat respiratory infections and that its usage increased significantly since the beginning of the study. Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to levofloxacin increased from 20% to 54% during the 5-year period. Based on these data, there is a greater likelihood of detecting which of the following in the latter isolates compared with the bacteria recovered at the beginning of the study?
B. Expression of carbapenemase
C. Expression of extended-spectrum β-lactamases
D. Mutation of the gene encoding dihydrofolate reductase
E. Mutation of the gene encoding elongation factor-2
F. Mutation of the gene encoding topoisomerase II
The graph shows the response elicited by different concentrations of drug X in a system containing spare receptors in the absence (solid curve) and presence (dashed curves) of two different concentrations of drug Y. Drug Y alone has no effect.
Which of the following best describes drug Y?
A. Competitive reversible antagonist
B. Full agonist
C. Inverse agonist
D. Noncompetitive antagonist
E. Partial agonist
A 42-year-old woman comes for a routine follow-up examination. She has an 8-year history of hypertension treated with a thiazide diuretic. She reports that she tires easily with exertion because of her weight but is otherwise asymptomatic. She drinks one to two glasses of wine weekly. There is no family history of liver disease. She is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 77 kg (170 lb); BMI is 29 kg/m2. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Examination shows no other abnormalities except for truncal obesity with no abdominal striae. Serum studies show:
Urea nitrogen: 19 mg/dLGlucose: 117 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1 mg/dL
Total cholesterol: 227 mg/dL
HDL-cholesterol: 32 mg/dL
Triglycerides: 347 mg/dL
AST: 87 U/L
ALT: 85 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's increased serum liver enzyme activity?
A. Alcoholic hepatitis
B. Hemochromatosis
C. Hepatitis A
D. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
E. Porphyria cutanea tarda
