- Joined
- Apr 16, 2016
- Messages
- 27
- Reaction score
- 22
- Points
- 4,601
- Pre-Medical
Hey Guys,
I was just going through my content review and found that I had a hard time memorizing the relationship between pH and pKa. Such as, if the pH is higher than the pKa then the solution is acidic and the side chain of the amino acid is deprotonated. So I made a memory device that I would like to share.
1) write pH and pKa in alphabetical order
2) Note that pH is refers to the solution and pKa refers the substrate.
3) draw arrow pointing from pH ----> pKa (make like an nucleophile electrophile, see drawing below)
Viola! as you can see,
if pH ---> pKa, the solution deprotonates the pKa (substrate), thus the solution is basic.
if pH <------ pKa, the substrates grabs the proton (is protonated) from the solution , thus the solution is acidic.
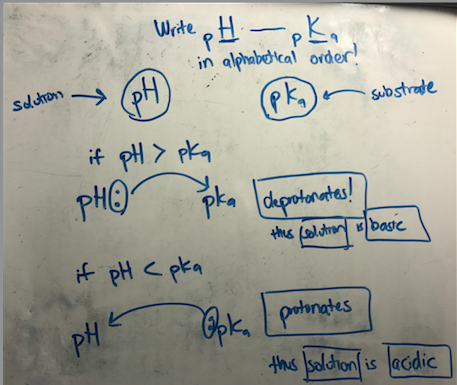
Thought that might help 🙂
I was just going through my content review and found that I had a hard time memorizing the relationship between pH and pKa. Such as, if the pH is higher than the pKa then the solution is acidic and the side chain of the amino acid is deprotonated. So I made a memory device that I would like to share.
1) write pH and pKa in alphabetical order
2) Note that pH is refers to the solution and pKa refers the substrate.
3) draw arrow pointing from pH ----> pKa (make like an nucleophile electrophile, see drawing below)
Viola! as you can see,
if pH ---> pKa, the solution deprotonates the pKa (substrate), thus the solution is basic.
if pH <------ pKa, the substrates grabs the proton (is protonated) from the solution , thus the solution is acidic.
Thought that might help 🙂
