The answer in blue is mine, which is wrong. Please give explanations for the right answers, if possible. Thank You...
3.
6.
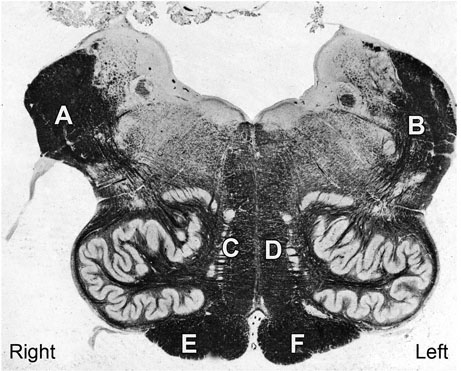
I chose C
Please give explanations for your reasoning. I'd greatly appreciate it.
1. A study is conducted to assess the effectiveness of a registry for identifying patients 50 years old and older eligible for colon cancer screening. Medical practices are selected based on equal and proportional representation of both genders and socioeconomic and ethnic groups, including those who have medical insurance and those who do not. Half of the practices will use the registry for a 15-year period and the other half will provide usual care without the registry during the same period. Results show that the colon cancer mortality rate is decreased in the practices using the registry, and the researchers recommend use of a patient registry to decrease the number of deaths due to colon cancer. Which of the following study characteristics most directly supports the researchers' recommendation?
A. Accuracy
B. External validity
C. Face Validity
D. Precision
E. Reliability
A. Accuracy
B. External validity
C. Face Validity
D. Precision
E. Reliability
2. An experiment is designed to study the differences between two tissue-specific isozymes of a particular enzyme. The Vmax of enzyme 1 is 300 units of activity per minute per milligram of protein, whereas the Vmax of enzyme 2 is 30 units of activity per minute per milligram of protein. Based on these numbers, which of the following conclusions about the Km values for enzyme 1 and enzyme 2 is most accurate?
A. The Km cannot be predicted based solely on the value of Vmax
B. The Km for enzyme 1 and the Km for enzyme 2 will differ but cannot be quantified with the given data
C. The Km for enzyme 1 is one-tenth the Km for enzyme 2
D. The Km for enzyme 1 is ten times greater than the Km for enzyme 2 (Is it this??)
E. They are the same
A. The Km cannot be predicted based solely on the value of Vmax
B. The Km for enzyme 1 and the Km for enzyme 2 will differ but cannot be quantified with the given data
C. The Km for enzyme 1 is one-tenth the Km for enzyme 2
D. The Km for enzyme 1 is ten times greater than the Km for enzyme 2 (Is it this??)
E. They are the same
3.
A 27-year-old man has had recurrent vesiculoulcerative lesions of the vermilion border of the lips over the past 6 months. The most likely causal virus remains latent in which of the following cell types?
A. Endothelial cell
B. Epithelial cell
C. Macrophage
D. Myocyte
E. Neuron (Is it this??)
F. Osteoclast
A. Endothelial cell
B. Epithelial cell
C. Macrophage
D. Myocyte
E. Neuron (Is it this??)
F. Osteoclast
4. A 9-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a 6-hour history of fever, headache, and stiff neck. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F). Physical examination shows nuchal rigidity and a diffuse nonblanching rash. A Gram stain of cerebrospinal fluid shows gram-negative intracellular diplococci. Which of the following components of this pathogen is used to determine serogroup specificity and is a component of the vaccine for this organism?
A. Capsule (Is it this??)
B. Lipooligosaccharide
C. Peptidoglycan
D. Pili
E. Porin Proteins
5. A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of fever and shortness of breath. He underwent bone marrow transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia 2 months ago. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), and respirations are 32/min. Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields on auscultation. A chest x-ray shows interstitial pneumonia. A photomicrograph of a biopsy specimen of the lung tissue is shown. Decreased function of which of the following most likely predisposed this patient to infection?
A. Dendritic cells
B. Eosinophils
C. Mast cells
D. Neutrophils
E. T Lymphocytes (Is it this??)
A. Capsule (Is it this??)
B. Lipooligosaccharide
C. Peptidoglycan
D. Pili
E. Porin Proteins
5. A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of fever and shortness of breath. He underwent bone marrow transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia 2 months ago. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), and respirations are 32/min. Diffuse crackles are heard over the lung fields on auscultation. A chest x-ray shows interstitial pneumonia. A photomicrograph of a biopsy specimen of the lung tissue is shown. Decreased function of which of the following most likely predisposed this patient to infection?
A. Dendritic cells
B. Eosinophils
C. Mast cells
D. Neutrophils
E. T Lymphocytes (Is it this??)
6.
A 25-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after sustaining blunt trauma to the abdomen in a motor vehicle collision. His blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg. Physical examination shows abdominal distention and diffuse tenderness mainly in the left upper quadrant. Bowel sounds are decreased. Which of the following sets of systemic responses is most likely to occur as a result of sympathetic reflex compensation induced by this patient's condition?
A. Arterial constriction / Venous constriction / Increase Heart rate (Is it this??)
B. Arterial constriction / Venous constriction / Decrease Heart rate
C. Arterial constriction / Venous dilation / Increase Heart rate
D. Arterial constriction / Venous dilation / Decrease Heart rate
E. Arterial dilation / Venous constriction / Increase Heart rate
F. Arterial dilation / Venous constriction / Decrease Heart rate
G. Arterial dilation / Venous dilation / Increase Heart rate
H. Arterial dilation / Venous dilation / Decrease Heart rate
A. Arterial constriction / Venous constriction / Increase Heart rate (Is it this??)
B. Arterial constriction / Venous constriction / Decrease Heart rate
C. Arterial constriction / Venous dilation / Increase Heart rate
D. Arterial constriction / Venous dilation / Decrease Heart rate
E. Arterial dilation / Venous constriction / Increase Heart rate
F. Arterial dilation / Venous constriction / Decrease Heart rate
G. Arterial dilation / Venous dilation / Increase Heart rate
H. Arterial dilation / Venous dilation / Decrease Heart rate
7. A 70-year-old woman comes to the physician because of frequent crying and difficulty sleeping since her husband died suddenly 3 weeks ago. She has had a 1.4-kg (3-lb) weight loss during this period. She appears tearful. There is no suicidal ideation. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial action by the physician?
A. Encouraging the patient to live with a relative
B. Providing supportive counseling
C. Recommending cognitive behavioral therapy
D. Prescribing antidepressant therapy
E. Prescribing long-acting benzodiazepine therapy (Is it this??)
8. A 55-year-old woman is brought to the physician because of a 6-month-history of progressive difficulty walking. Neurologic examination shows spasticity, hyperreflexia, and clonus in the lower extremities. Babinski sign is present bilaterally. A drug with which of the following mechanisms of action will most likely decrease the spasticity in this patient?
A. Activation of γ-aminobutyric acid receptors in muscle spindle afferents (Is it this??)
B. Activation of glutamate receptors in gamma motoneurons (or this??)
C. Activation of serotonin receptors in alpha motoneurons
D. Inhibition of glycine receptors in Golgi tendon organ afferents
E. Inhibition of nicotinic receptors in Renshaw cells
F. Inhibition of α2 receptors in excitatory interneurons
A. Encouraging the patient to live with a relative
B. Providing supportive counseling
C. Recommending cognitive behavioral therapy
D. Prescribing antidepressant therapy
E. Prescribing long-acting benzodiazepine therapy (Is it this??)
8. A 55-year-old woman is brought to the physician because of a 6-month-history of progressive difficulty walking. Neurologic examination shows spasticity, hyperreflexia, and clonus in the lower extremities. Babinski sign is present bilaterally. A drug with which of the following mechanisms of action will most likely decrease the spasticity in this patient?
A. Activation of γ-aminobutyric acid receptors in muscle spindle afferents (Is it this??)
B. Activation of glutamate receptors in gamma motoneurons (or this??)
C. Activation of serotonin receptors in alpha motoneurons
D. Inhibition of glycine receptors in Golgi tendon organ afferents
E. Inhibition of nicotinic receptors in Renshaw cells
F. Inhibition of α2 receptors in excitatory interneurons
9. An investigator is studying a large family with many members who are affected by a disorder caused by a fully penetrant autosomal dominant inherited gene mutation. A pedigree is shown. Most affected members also have a rare allele at a locus thought to be closely linked to the disease locus. A father (individual III-3) and his daughter (individual IV-3) have the disorder, but they have the wild-type allele at the linked locus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
A. Insertion of a LINE sequence
B. Random segregation
C. Recombination
D. Single nucleotide polymorphism
E. Transduction (Is it this?? Isn't this pedigree Autosomal Dominant??)
A. Insertion of a LINE sequence
B. Random segregation
C. Recombination
D. Single nucleotide polymorphism
E. Transduction (Is it this?? Isn't this pedigree Autosomal Dominant??)
10. A 16-year-old girl with type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the physician because of a 10-kg (22-lb) weight loss during the past 6 months. The patient reports that she is feeling fine, and she does not think that anything is wrong. She says that she is happy to have lost the weight, and she would like to lose more weight. She says that her diabetes has been in good control, and she is not aware of any insulin reactions. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and now weighs 46 kg (102 lb); BMI is 17 kg/m2. Physical examination shows no other abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%; 6 months ago, it was 5.8%. Which of the following patient behaviors most likely led to her weight loss?
A. Decreasing the amount of self-administered insulin dose
B. Overuse of laxatives
C. Restricting calorie consumption
D. Self-induced vomiting after meals (Is it this??)
E. Starting an intense aerobic exercise program
A. Decreasing the amount of self-administered insulin dose
B. Overuse of laxatives
C. Restricting calorie consumption
D. Self-induced vomiting after meals (Is it this??)
E. Starting an intense aerobic exercise program
11. A previously healthy 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of a 1-month history of excessive urination; she also has had a 2.3-kg (5-lb) weight loss during this period. Her pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 92/58 mm Hg. Physical examination shows poor skin turgor and a fruity odor to her breath. Her blood glucose concentration is 612 mg/dL. Which of the following is most likely to be decreased in this patient?
A. Arterial P CO2
B. Arterial P O2
C. Serum acetone concentration (Is it this??)
D. Serum potassium concentration
E. Serum triglyceride concentration
F. Serum urea nitrogen concentration
A. Arterial P CO2
B. Arterial P O2
C. Serum acetone concentration (Is it this??)
D. Serum potassium concentration
E. Serum triglyceride concentration
F. Serum urea nitrogen concentration
12. A 48-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of progressive ringing in her right ear. She also has felt dizzy while exercising. Neurologic examination shows dysmetria of the right upper and lower extremities. Muscle strength and somatosensory function testing of all extremities shows no abnormalities. Audiometry shows moderate hearing loss in the right ear. An MRI of the brain is most likely to show a mass compressing which of the following labeled structures in the photograph of a cross section of the brain stem?

I chose C
13. A 2495-g (5-lb 8-oz) female newborn is delivered at term to a 30-year-old woman who had no prenatal care. Physical examination of the newborn shows jaundice, nasal flaring, and grunting. Laboratory studies show marked anemia and hyperbilirubinemia. Further testing shows that the newborn is blood group O, Rh-positive, and the mother is blood group O, Rh-negative. Which of the following most likely mediated the transplacental transfer of the maternal factor causing this newborn's symptoms?
A. C3b receptor
B. Fc receptor
C. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor
D. α/β T-lymphocyte receptor
E. Transferrin receptor
A. C3b receptor
B. Fc receptor
C. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor
D. α/β T-lymphocyte receptor
E. Transferrin receptor
Please give explanations for your reasoning. I'd greatly appreciate it.
