- Joined
- May 23, 2013
- Messages
- 242
- Reaction score
- 23
Can anyone help answer these problems?
Number 76 asks for the structure of glycine at ph 7. I thought that since this is neutral PH, both groups would be non charged. However, the answer has the amino group charged as +1 and the carboylic end as -1. Can someone explain why?
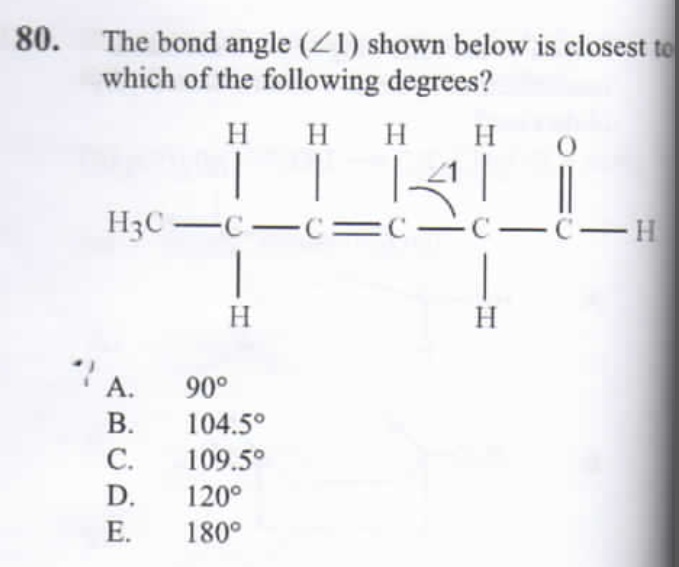
Number 80 asks to describe a bond angle on a carbon that is clearly sp3. I answered 109.5, however, the given answer is said to be 120 degrees. Anyone have any idea why?
I would normally post a picture, but I'm afraid to get sued by posting a pic xD
EDIT: I see my error in number 76. I am still unsure about number 80 though....
Number 76 asks for the structure of glycine at ph 7. I thought that since this is neutral PH, both groups would be non charged. However, the answer has the amino group charged as +1 and the carboylic end as -1. Can someone explain why?
Number 80 asks to describe a bond angle on a carbon that is clearly sp3. I answered 109.5, however, the given answer is said to be 120 degrees. Anyone have any idea why?
I would normally post a picture, but I'm afraid to get sued by posting a pic xD
EDIT: I see my error in number 76. I am still unsure about number 80 though....



 Thats what I thought. I was thinking of "n" in PV = nRT as opposed to V.
Thats what I thought. I was thinking of "n" in PV = nRT as opposed to V.