- Joined
- May 13, 2016
- Messages
- 77
- Reaction score
- 6
10) Acetic acid and ethanol react to form an ester product as shown below.
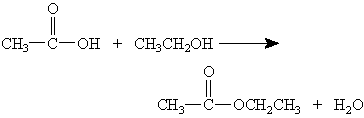
In determining which reactant loses the –OH group, which of the following isotopic substitutions would be most useful?
I might have the mechanism wrong but I thought that the -OH group in acetic acid is able to be the leaving group in this reaction so I chose A.
23) Which amino acid residues were incorporated into Compound 1 to promote the adhesion of cells on the scaffold surfaces?
What makes Asp and Arg the correct answer? What are these amino acids interacting with on the scaffold surfaces? What is a scaffold surface by the way?
45)
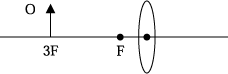
In the above figure, an object O is at a distance of three focal lengths from the center of a convex lens. What is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object?
Since this is a lens and the focus is on the same side as the object I denoted the focus to be negative and did the following steps:
1/f = 1/i + 1/o
1/(-f) = 1/i + 1/(3f)
1/i = -4/(3f)
i = -(3f)/4
M= -i/0 = -1/4 -->But 1/4 wasn't an answer so I used a positive value for the focus instead and got the correct answer of 1/2.

In determining which reactant loses the –OH group, which of the following isotopic substitutions would be most useful?
I might have the mechanism wrong but I thought that the -OH group in acetic acid is able to be the leaving group in this reaction so I chose A.
23) Which amino acid residues were incorporated into Compound 1 to promote the adhesion of cells on the scaffold surfaces?
What makes Asp and Arg the correct answer? What are these amino acids interacting with on the scaffold surfaces? What is a scaffold surface by the way?
45)

In the above figure, an object O is at a distance of three focal lengths from the center of a convex lens. What is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object?
Since this is a lens and the focus is on the same side as the object I denoted the focus to be negative and did the following steps:
1/f = 1/i + 1/o
1/(-f) = 1/i + 1/(3f)
1/i = -4/(3f)
i = -(3f)/4
M= -i/0 = -1/4 -->But 1/4 wasn't an answer so I used a positive value for the focus instead and got the correct answer of 1/2.
