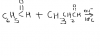- Joined
- Aug 15, 2010
- Messages
- 5
- Reaction score
- 0
What is the major product of the crossed aldol reaction shown below?
The reaction is in the attachemnts....
Can anyone guide me on how to approach this problem....
Thank You
The reaction is in the attachemnts....
Can anyone guide me on how to approach this problem....
Thank You
Attachments
Last edited: