- Joined
- May 27, 2012
- Messages
- 2,107
- Reaction score
- 4,666
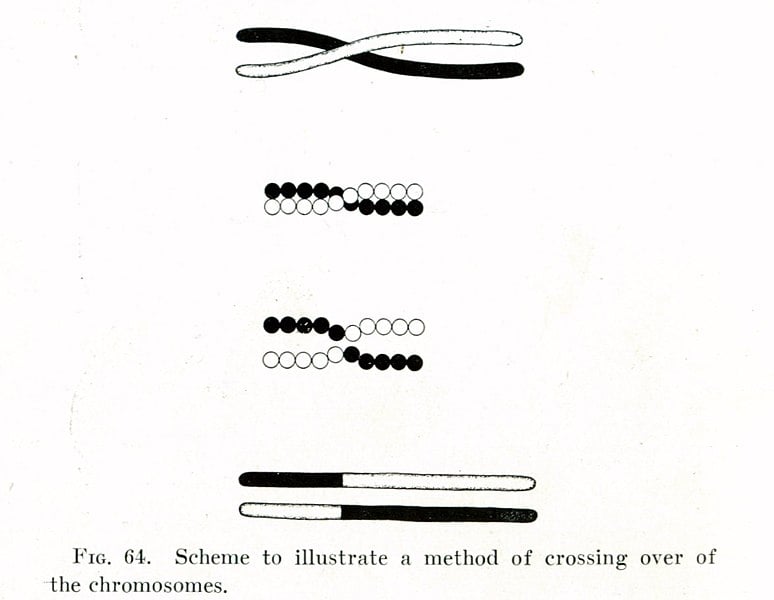
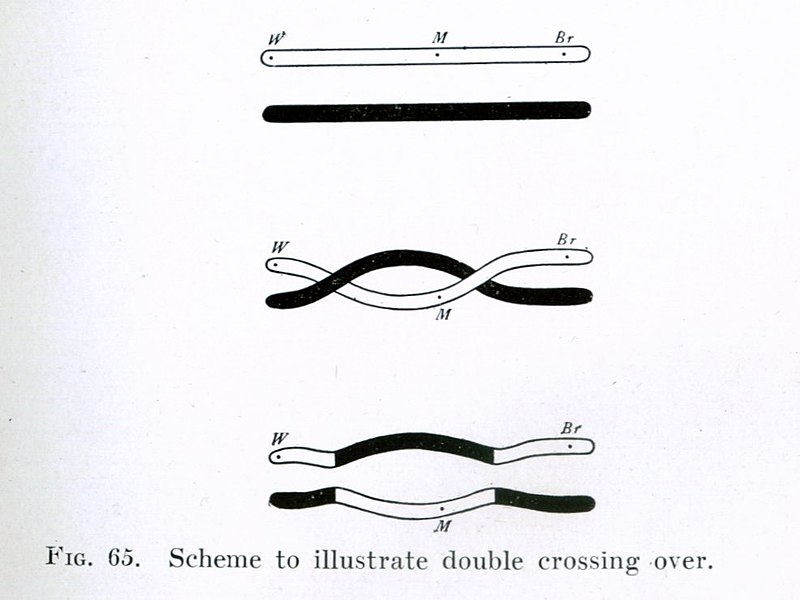
I missed a question regarding this in one of my practice exams.
I have searched for a while but cannot find a good source to learn about it.
What is the difference between the two and what do each mean?
Thank you very much!
I have searched for a while but cannot find a good source to learn about it.
What is the difference between the two and what do each mean?
Thank you very much!