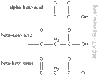D
dentalstudent2021
Hey guys. I understand that the alpha is first carbon from carbonyl group. but i don't understand when there are 2 carbonyls which is alpha (and then beta) .
picture attached of sample structure.
Thanks!
picture attached of sample structure.
Thanks!
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: