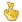Am trying Cindrella. This is what i could collate till the third week.. rest are following..
Day2 Embryo is at two cell stage
Day3 Morula is formed
day 4 Blastocyst is formed
Day8 Bilaminar disc
Placenta- trophoblast differenciates in cytotrophoblast n syncitiotrophoblast
Day 9 Placenta... Lacunae appears in syncytium
Day 11 embryo gets implanted in endometrium
Day 13 Placental primary villi form
Day14 Prochordal plate
Day 15 Primitive streak appears. Definitive yolk sack is formed
Day 16 Intra - embryonic mesoderm is formed/ disc is now 3 layered. placental secondary and tertiary villi seen. GI - allantoic diverticulum starts appearing
Day 17 Notochord process appears. Heart tube is seen in cardiogenic area. Allantoic diverticulum is seen.
Day 19 Intra embryonic mesoderm is being formed . Connecting stalk can be distinguished
Day21 Neural groove is seen.
Third week events Head fold begins to form. Neural tube begins to form. Hypophysis- Infundibular diverticulum develops
Gut begins to acquire tubular form with head and tail foldings.
Hepatic bud appears. Also the pancreatic bud appears thereafter.
CVS - Blood and vessel forming cells ( angioblastic islands) appear. The cardiogenic area, hard tube and pericardium have formed.
Urogenital... intermediate mesoderm formed. External genitalia begin to form
Day 23 Closure of neural tube is seen.
Day2 Embryo is at two cell stage
Day3 Morula is formed
day 4 Blastocyst is formed
Day8 Bilaminar disc
Placenta- trophoblast differenciates in cytotrophoblast n syncitiotrophoblast
Day 9 Placenta... Lacunae appears in syncytium
Day 11 Embryo gets implanted in endometrium
Day 13 Placental primary villi form
Day14 Prochordal plate
Day 15 Primitive streak appears. Definitive yolk sack is formed
Day 16 Intra - embryonic mesoderm is formed/ disc is now 3 layered.
Placental secondary and tertiary villi seen.
GI - allantoic diverticulum starts appearing
Day 17 Notochord process appears.
Heart tube is seen in cardiogenic area.
Allantoic diverticulum is seen.
Day 19 Intra embryonic mesoderm is being formed.
Connecting stalk can be distinguished
Day21 Neural groove is seen.
Other Third week events
Head fold begins to form.
Neural tube begins to form.
Hypophysis- Infundibular diverticulum develops
Gut begins to acquire tubular form with head and tail foldings.
Buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures (end of third week)
Hepatic bud appears.
Also the pancreatic bud appears thereafter.
CVS - Blood and vessel forming cells (angioblastic islands) appear.
The cardiogenic area, hard tube and pericardium have formed.
Urogenital... intermediate mesoderm formed. External genitalia begin to form
Fourth Week:
Day 22: Pharyngeal Arches appearance of first ands second arch. Appearance of Optic Sulcus (Eye). Ear: Otic Placode Seen.
Day 23: Closure of neural tube. Primordial sensory ganglia formed (spinal and cranial)
Day 25: Closure of anterior neuropore
Day 26: Skeleton: Forelimb Bud appears
Day 27: Closure of posterior neuropore
Day 28: Skeleton: Hind limb Bud appears
Most cranial pairs of cervical ganglia formed.
Tongue starts forming (2 lateral swellings and Tuberculum Impar)
Fusiform shape of the stomach becomes visible
Septum Transversum (Diaphragm) established.
Tracheobronchial diverticulum formed.
CVS: Heart & Pericardium lie ventral to foregut. Subdivisions of heart are visible
Heart begins to Beat (Becomes functional)
Formation of septa in the heart begins
Aortic arches appear (Cranial to caudal)
Most of first aortic arch disappears by the end of fourth week.
Veins start forming
Urogenital: Pronephric tubules forming. Regress by end of fourth week.
Mesonephric tubules forming. Uro-rectal septum begins.
Hypophysis: Rathkes Pouch protrudes from Stomatodeum
Eye: Optic vesicle contacts surface ectoderm. Lens Placode forming.
Fifth Week
Day 29: Four Pharyngeal arches are seen
Skeleton: Limbs become paddle shaped.
Hypobranchial eminence visible
Caecal Bud identified.
CVS: Spiral Septum Formed. Aortic arches complete. Lymphatic sac formed. Cardinal, Vitelline and Umbilical veins formed. Conduction system formed.
Urogenital: Metanephros is formed.
CNS: Formation of Brain Vesicle. Sympathetic ganglia formed. Cerebral hemispheres begin to form
Adrenal Gland begins to form
Eye: Eye primordium surrounded by loose mesenchyme
Ear: Auricle starts forming
Sixth Week
Day 36: Skeleton: Formation of Digits
Cartilaginous models of bone start forming
Dental Laminae of upper and lower Jaw established
GI- Intestinal loops well formed.
Urorectal septum starts dividing the cloaca.
Allantois and appendix become differentiated.
Diaphragm descends to thoracic level.
Stomach completes its rotation.
CVS: Coronary circulation established. AV Valves and Papillary muscles formed.
Urogenital: Metanephros is formed. Cloacal membrane divides into Urogenital and anal membranes
Eye: Choroid fissure formed. Lens vesicle seen.
Ear: Cochlea and Semi-circular canals forming.
Seventh Week:
Salivary Gland appears
Thyroid Gland reaches its definitive position.
Rotation of limbs occurs
Separation of cloaca into rectum and urogenital sinus
Intestinal loop herniates out of abdominal cavity
Fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreas.
Heart Septa are fully formed.
Urogenital: Urogenital sinus formed
Eye: Solid lens formed.
Eighth Week:
Dental: Enamel organs are formed
GI: Intestinal loop rotates counter-clockwise
CNS: Cerebellum starts forming.
Day 50: Elbow and knee established.
Fingers and Toes are free.
Primary centers of ossification are seen in few bones.
Placenta- Villi are seen all around the trophoblast
Hypophysis: Rathkes pouch loses connection with oral cavity.
Ear: Cochlea and Semi-circular canals reach definitive form.
Ninth Week
Anal membrane breaks down
Tenth Week
Enamel organ becomes cup shaped
CNS: Corpus Callosum Formed
Ear: Scala Vestibuli and scala tympani formed.
11 Week
12 Week
Formation of tonsils
Primary centers of ossification in all long bones.
Head and tail folding are completed.
Herniated coils of intestine return to abdominal cavity.
Bile formation starts.
Pancreatic islets formed.
Urogenital: (9-12 weeks) Urethral folds fuse with each other. Prostate begins.
Definitive Kidney (metanephros) becomes functional.
CNS: Cerebellar cortex and Purkinje cells formed.
13 Week
14 Week
15 Week: CNS: Dentate Nucleus seen
16 Week: Definitive Placenta Formed.
Nerve Myelination begins
18 week
20 week: Tonsil infiltrated by lymphoid tissue
Insulin secretion begins
Vagina gets canalized.
24 week: Enamel and dentine formed
Tongue formation complete
28 week: Ear: External acoustic meatus canalized.
30 week:
32 week: Sulci and gyri start appearing on brain surface.
34 week
36 week
38 week
40 week